A enormous lighthouse towering above the seaside, standing strong against decades of salt-laden sea winds and blinding rains, remains as solid as possible. Or perhaps that very ordinary metal mail box in your garden has stood there for a thousand seasons without developing any rust.
The unsung hero in all of this is galvanizing technology. From a huge infrastructure development to an everyday small thing, selecting the right galvanized metal is what makes it last and hold its worth.
For sheet metal manufacturing projects, the best choice of galvanized metal has a critical influence on product longevity and cost. This guide will help you select the right metal for galvanizing for your project, resolving any doubts you may have during the selection process, allowing it to be easy to select the best galvanizing option for your project.
Core Answer Summary
| Core Module | Key Information | Applicable Scenarios / Precautions |
| Galvanizing Process Selection | Hot-dip galvanizing (50-100μm, strong protection), electroplating (8-20μm, high precision), powder sherardizing (no hydrogen embrittlement). | Hot-dip galvanizing is used for large parts, electroplating is used for precision parts, and powder sherardizing is used for complex parts. |
| Galvanizing Substrate Selection | Preferred are low-carbon steel (≤0.25% carbon, Q235/SPCC), low-alloy steel with controlled manganese and silicon, high-carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum alloys are not recommended. | Low-carbon steel is suitable for sheet metal fabrication parts such as agricultural machinery housings and building connectors. |
| Galvanizing Standard Selection | G60 (85μm, mild corrosion); G90 (127μm, moderate corrosion), G115 (165μm, severe corrosion). | G60 is used indoors, G90 is used for outdoor shelters, and G115 is used near the sea/in humid farmland. |
| Galvanized Steel vs Stainless Steel | Galvanized steel has low cost (US$2-5/year) lbs, requires maintenance). Stainless steel is corrosion-resistant ($8-15/lb, low maintenance). | Galvanized steel is recommended for budget-conscious users; stainless steel is recommended for highly corrosive environments. |
Does Your Project Need Galvanizing? JS Answers
When seeking a galvanizing company for your sheet metal fabrication project, do you fear that inexperience by the service company will result in an inappropriate solution?
JS has over 15 years of experience in sheet metal working and galvanized metal applications, our engineering team holds the NACE international coating inspector certification and has a deep involvement in the development and discussion of ASTM galvanizing standards.
We have provided reliable custom sheet metal fabrication manufacturing services for more than 5000 customers in industries such as automotive manufacturing, agricultural machinery, and building structures. Among them, the top three agricultural machinery enterprises in the world have been continuously supplied for 8 years.
The cumulative delivery of galvanized structural components exceeds 200000, and the product defect rate is consistently controlled below 0.5%. Galvanized connectors provided for a certain offshore wind power project last year passed a salt spray test of 2000 hours, far exceeding the industry standard.
It is worth mentioning that we have established a complete database of galvanizing processes, including 287 matching schemes for materials and galvanizing processes.
In response to customer inquiry, the system can automatically retrieve similar case data such as the type of sheet metal fabrication parts you need and generate a technical solution containing zinc layer thickness suggestions, predictable lifespan, and cost analysis within 10 minutes. That means every suggestion you get has already been validated in dozens of similar projects.
JS offers sheet metal fabrication and metal for galvanizing services. We can customize solutions based on project specifications, providing unique support from consultation to solution confirmation. Delivery is 7-10 days after receiving an order.
What Is Galvanizing And How Does It Give Deep Corrosion Protection And Enhance Performance?
Following the reading on JS's experience, you might have asked, what is galvanizing? How can it give deep corrosion protection to sheet metal fabrication parts? The following is a general introduction from three angles:
Definition and Major Principles of Galvanizing
Galvanizing is a process of forming a continuous zinc coating over the surface of a metal substrate by physical or chemical means. The main protective action is the "sacrificial anode effect":
Zinc is more electrochemically active than iron and preferentially oxidizes when exposed to corrosive media. Oxidation forms a compact composite layer shielding the substrate from corrosive media and preventing rusting.
Performance improvement of Galvanizing on Components of Sheet Metal Fabrication
Beyond basic corrosion protection, galvanizing can improve component performance in several ways:
- In wet conditions found in agricultural environments, galvanized coating will extend the lifespan of non-coated components by 5-10 years.
- Zinc coating is twice as hard as mild steel, reducing scratches during shipping and installation.
- The galvanized coating is exceptionally paintable and weldable, allowing for seamless connectivity without additional treatment, reducing processing complexity.

Demystifying The Core Galvanizing Process: Hot-Dip Vs. Electroplating
Since we have understood the purpose of galvanizing, let us observe the differences among the three galvanizing processes from the process, characteristics, and application areas points of view to guide you in choosing the right one:
Comparison of Core Parameters of the Three Galvanizing Processes
| Process Type | Core Process | Coating Thickness | Coating Adhesion | Applications |
| Hot-Dip Galvanizing | Degreasing of the substrate → Pickling → Electroplating → Immersion in molten Zinc at 450°C → Cooling. | 50-100μm | Extremely strong (Zinc-Iron Alloy Layer Bonding). | Large structural parts, outdoor equipment. |
| Electro galvanizing | Pretreatment of the substrate → Tank electroplating energizing → Zinc layer formation → Post-passivation treatment. | 8-20μm | Reasonably strong (physical adsorption + chemical bonding). | Precision components (electronic casings, robot joint components). |
| Powder Sherardizing | Cleaning of substrate → Sealing and mixing with zinc powder → Heat at 300-400°C → Zinc atoms diffuse into a layer. | 10-50μm | Extremely strong (Atomic-level diffusion bonding). | Components with complex shapes, high-strength bolts. |
Advantage and considerations of the three processes
- Hot-dip galvanizing: High strength, low maintenance, requires adjustment to zinc pot size and slightly deforms when cooling.
- Electrogalvanizing: Uniform coating, very high accuracy, cavities with complex details require setting of the electrode to avoid irregular coating.
- Powder sherardizing: No hydrogen embrittlement, full coverage, processing cycle is long (24-48 hours), and the cost is slightly more.
JS offers hot-dip galvanizing and electrogalvanizing services. We can recommend the optimum solution according to your metal for galvanizing requirements. 7-10 day delivery from the order date is offered effectively to meet project timelines.
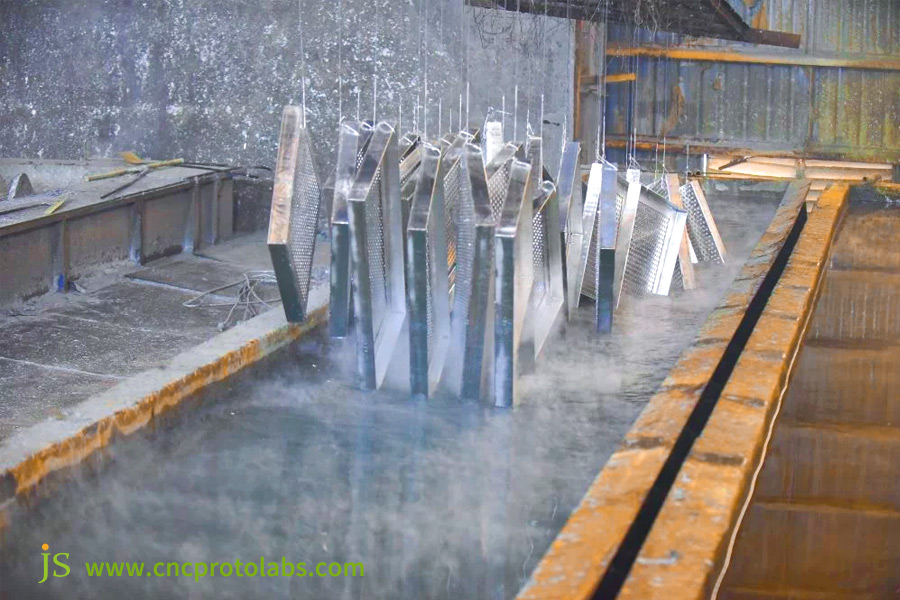

Choice Of Metal For Galvanizing Substrate: Which Metals Are Appropriate For Galvanizing?
Commonly Galvanized Substrate Properties and Applications
Low-carbon steel (carbon content ≤ 0.25%) is used most commonly as a substrate. It is compatible with zinc well, is free from cracks, and is cost-effective (around $1.5-3/lb). Q235, SPCC, and 1010 are typical grades. It can be employed in most sheet metal fabrication parts, such as in agricultural machinery housings and connectors for buildings.
Low-alloy steel (alloying elements ≤ 5%) may be galvanized, but manganese (≤ 1.5%) and silicon (≤ 0.3%) must be controlled to avoid affecting adhesion of the zinc coating. It is best suited for outdoor guardrail brackets and heavy equipment bases.
High-carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum alloys are not to be employed: high-carbon steel is prone to cracking and does not bond well with the zinc coating, stainless steel is corrosion-resistant anyway, so galvanizing will be unnecessary, aluminum alloys form a brittle zinc alloy with an effect on mechanical properties.
Principles of Substrate Selection
The selection of substrate must be compatible with the service conditions:
- In humid and severely corrosive environments, low-carbon steel coated with heavy zinc is recommended.
- If there is a need to balance cost and performance, and no need for high strength, low-alloy steel does not need to be selected.
- For welding, in subsequent processing, low-carbon steel must be selected due to its better weldability and capability of easy repairing after galvanizing.
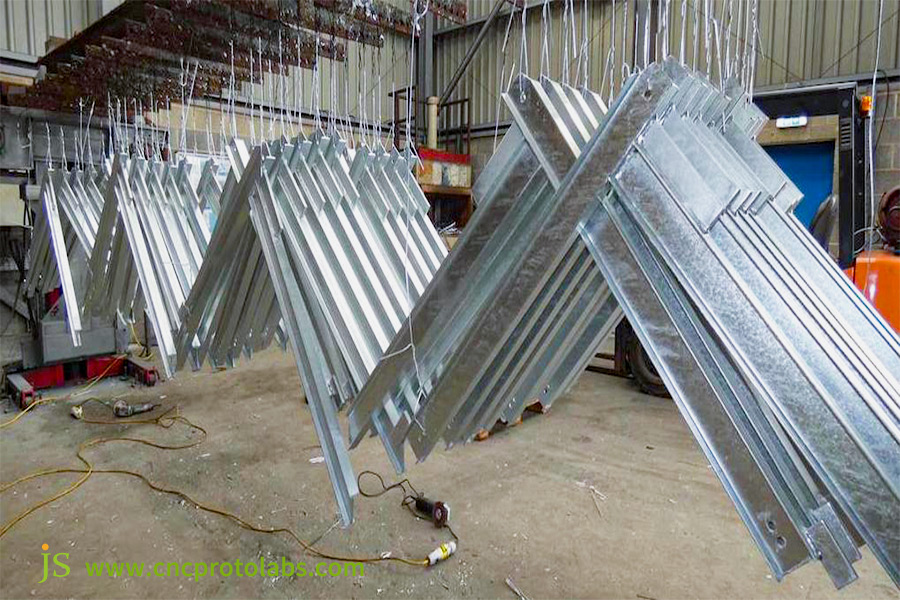

Passport Of Coatings: Types And Standards Of Galvanized Coatings
Having chosen the substrate and process, the standard and type of galvanizing coating are most important for quality. The below outlines thickness, surface treatment, and testing:
General Galvanizing Thickness Standards (G Series) and Available Applications
| Coating Grade | Double-Sided Zinc Coating Weight (oz/ft²) | Approximate Thickness (μm) | Available Environment | Typical Uses |
| G60 | 0.60 | 85 | Mild Corrosion (Indoor Dry Spaces, Offices). | Indoor Distribution Boxes, Furniture Brackets. |
| G90 | 0.90 | 127 | Moderate Corrosion (Outdoor Sheltered Places, Under Eaves). | Outdoor Billboard Signs, Balcony Railings. |
| G115 | 1.15 | 165 | Severe Corrosion (Coastal Areas, Wet Agricultural Fields, Chemical Industry Area). | Coastal Lighthouses, Agricultural Robot Cases. |
Galvanizing Surface Treatment Processes and Applications
The surface treatment of galvanized layer includes passivation and oil coating.
Passivation is divided into blue, color, and black:
- Blue passivation offers a blue film over 30% increased corrosion resistance, suitable for agricultural machinery and outdoor components.
- Colored passivation produces an iridescent coating with high decorative effect and fingerprint resistance, suitable for domestic appliances and electronic components.
- Black passivation produces black coating, suitable for concealed or light-shielded parts (internal equipment brackets, for instance).
Oiling is used primarily to prevent transport scratches and provide a temporary moisture protection, additional painting requires degreasing.
Galvanized Coating Testing Standards
Galvanizing thickness must be measured with magnetic thickness gage at least five points per square meter and average must comply with the standard. Adhesion must be verified in cross-hatch test (no peeling on 1mm×1mm grid) or bend test (no crack at 180°).
Corrosion resistance must be verified in salt spray test according to ASTM B117. G60 takes 48 hours to show no white rust, while G90 takes 72 hours to show no white rust.
Galvanized Steel Vs. Stainless Steel: How To Choose?
Galvanized steel and stainless steel are both utilized for sheet metal fabrication projects, and the choice between the two needs prudent analysis of some parameters:
Comparison of Core Parameters of Galvanized Steel and Stainless Steel
| Comparison Dimensions | Galvanized Steel (Mild Carbon Steel + G90 Galvanizing) | Stainless Steel (Type 304) |
| Initial Cost | Low ($2-5/lb) | High ($8-15/lb) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Dependent on zinc layer, outdoor lifespan of 15-20 years. | Self passivating, with a maintenance free lifespan of 30-50 years. |
| Processing Difficulty | Easy (cutting, bending, welding, then galvanizing). | Medium (uses stainless steel welding wire, susceptible to thermal deformation). |
| Weight | Density 7.85g/cm ³ | Density 7.93g/cm³ |
| Surface Appearance | Silver-gray (possibly passivated for color change). | Bright silver (possibly brushed or polished). |
Selection Recommendations
- Low Cost + Mild Climate: Galvanized steel (such as agricultural machinery components and brackets), which can reduce the cost of 1000 sets of shells by 6-8 thousand US dollars.
- High Corrosion + Not To Be Repaired: Stainless steel (coastal equipment, chemical parts). Zinc-rich coating must be repainted every 5-8 years if galvanized steel is used in order to prevent galvanized metal rust that destroys its service life.
- Domestic Decoration: Choose stainless steel or color passivated galvanized steel (50% cost saving).
JS can give suggestions of stainless steel and galvanized selection according to your project budget and application environment. JS also offers custom sheet metal fabrication manufacturing services, which ensure accurate processing of galvanized and stainless steel components.
Designer's Must-Read: Key Design Considerations For Galvanized Metal
When using galvanized metal for sheet metal fabrication, it is necessary to optimize the design in terms of process adaptation, protection, and efficiency:
Key Design Issues for Hot-Dip Galvanized Components
Avoid hot-dip galvanized components to be airtight enclosures because nuisance zinc readily causes deformation or nodules. Vent holes with a minimum diameter of 10mm should be included, located at the bottom of the cavity.
Keep component thickness variation. Suggested thickness variation for the same component is ≤ 3 times. Heating slits should be provided in the case of welding thick plates so that not due to uneven heating and cooling, deformation occurs.
The welding area should leave a space of ≥ 5mm for easy application of zinc rich paint, and avoid corners to prevent defects caused by zinc accumulation.
Key Design Points for Electrogalvanized Components
Electrogalvanized components should be avoided from deep cavities. Depths of deep cavities should be ≤ 3 times diameter. Auxiliary electrode holes should be provided for an even current flow and to avoid a non-uniform coating.
Corners should be radiused to ≥0.5mm to avoid the current concentration at acute corners, which could result in "burrs" and affect precision and safety.
General Design Principles
Galvanized component designs should be as simple in shape as possible. Complex pieces should be dismantled into separable forms to facilitate an even zinc coating. Exterior pieces should be equipped with drainage holes ≥5mm at the lowest point to keep water from coming into contact with the substrate over the long term, triggering galvanized rusting and subsequent corrosion.
JS possesses a professional design assistance team that can render suggestions for design optimization of your galvanized sheet metal fabrication job. With our online sheet metal fabrication services, you can upload your design drawings online and receive a quote and solution feedback within 24 hours.
More Than Just Sheet Metal: Selecting The Right Form Of Galvanized Metal For Your Project
Galvanized metal type determines processing efficiency and cost. The following comparison of features, scenarios, and costs will help you make a decision:
Comparison of Four Typical Galvanized Metal Forms
| Form Type | Processing Process | Benefits | Limitations | Suitable Applications |
| Galvanized Prefabricated Components | First process into parts → Galvanize the complete part. | Total zinc coating and long-lasting protection. | Long lead time (10-15 days), expensive shipping for large parts. | Complex sheet metal fabricating parts (agricultural equipment supports, equipment frames). |
| Galvanized Coil/Sheet | Galvanized first → cutting, bending, stamping. | High efficiency (1-3 days) and fairly low cost. | Replenishment of zinc required at bends and cuts. | Plain parts (distribution box panels, farm equipment covers, roof panels). |
| Galvanized Pipe | Bent steel pipe → galvanized → threaded and cut. | Inner wall can be galvanized to resist corrosion on the inside. | Zinc coating easily cracks when bent. | Exterior water pipes, equipment mounting pipes. |
| Galvanized Wire | Steel wire drawn → galvanized → trimmed and formed. | Even coating, smooth finish, suitable for small items. | Limited application | Small springs, outdoor fencing, hooks. |
Form Choice Decision Factors
- Component Complication: Use prefabricated components for complex components, use coils/sheets for simple components.
- Batch Production: Use coils/sheets for simple components with lot sizes >1,000. Sheet metal fabrication prices are 15-20% lower.
- Conditions of Transportation: Choose coils/sheets for large, distant shipments. Location fabrication is cost-saving.
JS offers galvanized metal fabrication in various shapes. We can recommend the most suitable shape based on your project size and timing requirements. We also provide transparent sheet metal fabrication price so that you are aware of what you are paying for.
Case Study: Guardian Of Weather-Resistant Robotic Joints In Agriculture
Client Background and Requirements
An leading agricultural technology company was developing a next-generation autonomous seed robot. Its core arm joint housing and internal structural components (critical sheet metal fabrication parts) faced three primary challenges:
- Harsh Environment: They were required to be exposed to wet fields and dry-outside conditions for extended periods of time, requiring parts to be highly corrosion-resistant.
- Precision and Durability: Arm joints had to be moved on a regular basis, with the requirement of component precision to ±0.1mm and trouble-free operation for at least five years.
- Overall Cost: The customer wishes to keep the cost of a single set of components within $100, so that it would remain under the project budget.
Challenge Analysis
The client presented three alternatives in the first case, each of them problematic:
- Stainless steel: Strong corrosion resistance, but at a price of $180 per unit in the first place, much more than the budget.
- Painted common carbon steel: Cheap price (around $60 per unit), but easy flaking of the paint in humid conditions with little resistance to corrosion and 1-2 years working life.
- Hot-dip galvanizing: Sufficient protection, but 60μm coating thickness increases component weight, impacts robot dexterity, and difficult to provide required precision.
JS Solution
JS team developed a solution that met the customer specifications:
- Process Innovation and Selection: We proposed and utilized electrogalvanizing, a process that employs an ultra-thin(around 8-12μm), consistent coating. This provides component precision without contributing unnecessary weight.
- Materials and Post-Processing: High-carbon content low-carbon cold-rolled steel of excellent quality was used as the substrate, and was subject to blue passivation treatment subsequent to galvanizing for the purpose of increased corrosion resistance.
- Stringent Quality Control: SC 2 (5-15μm) grade coating as per ASTM B633 was specified, and corrosion resistance was also tested through salt spray testing with a minimum rust-free period of 96 hours.
Final Results
- Accuracy: The electrogalvanized parts had a ±0.05mm measurement tolerance, which was still within robotic arm movement capacity.
- Cost Saving: The unit cost was lowered to $85, which was below the customer's budgetary limit.
- Life Expectancy Guaranteed: Operating in a humid farmland environment for 3 years without significant corrosion and requiring no maintenance.
- Identification by Vision: The blue passivated appearance becomes the professional brand logo of the product, enhancing its recognition.

Shopping List: How To Purchase The Correct Galvanized Metal
When you are ready to purchase galvanized metal, having the right shopping list will avoid mistakes and have you purchasing the correct product:
1. Establish Project Requirements: Familiarize yourself with galvanized metal form (e.g., sheet metal, pre-fabricated), quality of coating (e.g., G60, G90), substrate (e.g., mild steel), and size of the component, tolerance requirements, and exposure to the environment.
2. Locate Experienced Suppliers: Select experienced suppliers who possess high business acumen and ability to give quality inspection reports in order not to purchase low-quality products.
3. Negotiate on Delivery Date and After-Sales Service: Negotiate a proper delivery date as per the project schedule and inquire whether the supplier gives information regarding zinc coating repair service and returns and exchanges in the event of any shortfalls of quality.
4. Price Breakup Details: Request the supplier to provide a sheet metal fabrication price breakdown, including substrate cost, charge for galvanizing process, and post-process charge, to ensure that there are no hidden costs.
FAQs
Q1: Is galvanizing and "aluminum-zinc coating" (such as Galvalume) essentially the same?
No. Galvalume is a 55% aluminium, 43.4% zinc, 1.6% silicon alloy coating as opposed to regular galvanizing. It is more heat-resistant (able to resist heat up to 315°C) and cut-edge corrosion-resistant than regular galvanizing. It is generally applied in sheet metal fabrication processes like roofing and wall cladding, and is a high-performance alternative to some easy-cut or high-temperature applications.
Q2: How long will galvanized steel last?
It's an "it depends" type of question. Dry indoor conditions will see G60-grade galvanized steel last more than 30 years. Sheltered outdoor conditions will have G90-grade galvanized steel lasting 15-20 years. In heavily corrosive conditions, e.g., in the vicinity of sea, G115 would be used with a working life of around 8-12 years. It can be prolonged through maintenance.
Q3: If my galvanized part is going to be punched or cut, how do I prevent rust at the impacted area?
Machining inevitably damages the zinc coating, exposing the underlying material to the elements. If left untreated, this can lead to rust at the impacted area. This requires post-repair treatment. The most common practice is the use of zinc-rich paint with a high zinc content (≥95%). The damaged part must be cleaned of oil and contaminants before painting to allow for good adhesion between the base metal and the paint.
Summary
The choice of metal for galvanizing is not simply a matter of easy materials purchasing, it is a decision with serious implications on project safety, project length, and profit bottom line.
Whether precision parts for farm robots or massive structural bracing beams for high-rise buildings, just follow the guidelines and pair them with professional online sheet metal fabrication services, you can find the most suitable solution.
JS offers full-service custom sheet metal fabrication manufacturing, from consultation to choose galvanized metal to delivery of finished goods, to meet the needs of projects in a variety of industries. Welcome to choose JS and start your galvanized metal project. While ensuring a high cost-effective sheet metal fabrication price, you can also obtain high-quality sheet metal fabrication parts.
Disclaimer
The contents of this page are for informational purposes only.JS servicesThere are no representations or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that a third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design characteristics, material quality and type or workmanship through the Jusheng Network. It's the buyer's responsibilityRequire parts quotationIdentify specific requirements for these sections.Please contact us for more information.
JS Team
JS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. We have over 20 years of experience with over 5,000 customers, and we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal manufacturing,3D printing,Injection molding,Metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with over 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers, ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it is small volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseJS TechnologyThis means selection efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, visit our website:www.cncprotolabs.com